Green IoT-Smart Solutions for Sustainable Development
- {{"article.by"|translate}} Mila Velkovska
- {{"article.posted"|translate}} 25-01-2021
Green IoT-Smart Solutions for Sustainable Development
The Internet of Things is one of the driving technologies of Industry 4.0. It describes interconnected computer devices, machines, objects and people that share information through the internet, without human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
Green IoT is the future towards ecological, sustainable and environmentally friendly world. The “greening” itself includes efficient and effective design, manufacturing, use and disposal of servers, computers, printers, monitors and similar devices. The main goal is: minimal or no impact on the environment. Experts in developing centres strive to find alternative energy sources, to change the view of the world with higher environmental awareness and to minimize the damage that has occurred through the process of digitalization.
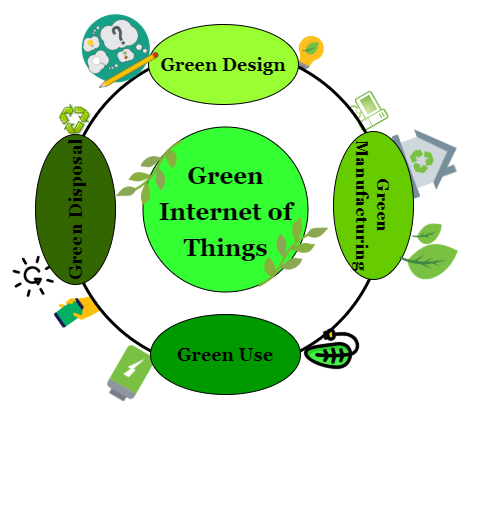
What exactly does Green IoT mean?
Green Design
From the very first steps in the process of creating a product, bigger attention should be paid to its lifespan. The design itself should offer durability and the possibility to reuse and recycle, so the electronic devices would circulate longer. The design process should take into account the materials that will be used. Sensors, actuators, RFID are just some of the components that enable IoT, and they should be designed to perform the same activities with reduced environmental impact. Moreover, the green design offers decreased hardware components and devices created with fewer non-degradable materials.
Green Manufacturing
Green manufacturing means improving the manufacturing processes so they will leave minimal impact on the environment. This part of the greening of IoT might be the easiest one to achieve because every company strives for energy-efficient manufacturing and minimal waste. Furthermore, integrated quality standards and durability policies in the whole production system could help the implementation of green manufacturing.
Green Use
Smart devices supported exactly by IoT have some characteristics that enable them to react to the real world in real-time and to predict its users’ needs. Also, they have a pretty complex structure and perform activities without human intervention-although it is not fully excluded. According to this, by measuring and regulating different physical parameters, smart devices offer numerous advantages that affect the environment and lead to reasonable use of the resources. Green use in this context refers to the additional upgrade of smart devices that will reduce energy consumption. That can be achieved with an automatic shutdown of components when not in use, integrating power-saving mode and principles that enable sleep-awake mode in electronic components.
Green Disposal
One of the primary goals in recent years has been to raise awareness that the product’s lifespan shouldn’t end when it is no longer used. Every product consists of components that can be reused for creating either the same or new product. According to numerous researching, the Earth is suffocating in electronic waste. World Economic Forum reveals that global recycling is relatively small. The EU is considered to have a leading position in terms of e-waste recycling and even within it, only 35% of the waste is officially recorded as properly collected and disposed. On a global level, for 80% of the e-waste, it is unknown how or where it is disposed-probably in a landfill. This is a significant problem as electronic components are not biodegradable.
Green disposal requires working on decomposing and disassembly, so components from old products will be reused to create new ones. Investments should be made in removing metals and minerals from e-waste so they can be returned in the manufacturing process. Hence, the process goes back to designing products with already (partially) provided materials.
-
Climate finance
21-01-2022 -
Tackling Climate Change & Air Pollution in the City of Skopje
30-04-2018 -
Tackling Climate Change & Air Pollution in the City of Skopje
22-03-2018 -
Micronarratives
08-06-2022
{{"article.lastestPosts"|translate}}
-
The Chamber of Commerce of North Macedonia has created the first decarbonization guide for small businesses in the country
30-10-2025 -
COP29 UN Climate Conference Agrees to Triple Finance to Developing Countries, Protecting Lives and Livelihoods
02-12-2024 -
We are building partnerships to implement a just energy transition
06-12-2023 -
Energy transition will be accelerated through the Green Financing Facility
06-12-2023




 Мод за знаковен јазик
Мод за знаковен јазик Говорен асистент
Говорен асистент Означи линкови
Означи линкови

 Зголеми маус
Зголеми маус