OPPORTUNITIES RISING FROM CIRCULARITY
Circular economy concept is based on the initiatives along the entire life cycle of the products, targeting their eco-design, promoting circular economy processes, fostering sustainable value chain, sustainable consumption and keeping used resources in the economy for as long as possible.
Circular economy concept is based on the initiatives along the entire life cycle of the products, targeting their eco-design, promoting circular economy processes, fostering sustainable value chain, sustainable consumption and keeping used resources in the economy for as long as possible. The main challenges of circularity in this economic model are:
- keeping materials at the highest possible value along the value chain,
- entire value chain matters, more than each stage individually,
- all stakeholders are engaged in changing the system,
- lifecycle thinking enables the identification of strategic points from design phase to the disposal,
- disconnect natural resources using and environmental impacts from economic activity and human well-being is essential.
The visualization of the circularity of this concept can be presented from ecological view as a circle of nature and from technological view as a network of interconnection.
At the Figure 3, grey line presents linear economy model with linearity connection between four economic steps of value chain: extraction of raw materials, production of goods, using of goods (products) and end-of-life by disposal of goods.
Circular economy model is based on circularity between four economic steps of value chain: extraction, production, using and end-of-life. Circularity builds upon value retention loops through follow processes (Fig.3):
- User-to-user processes: shorter loop, where a product or component remains close to its user and function (Fig.3, presented in purple).
- User-to-business processes: medium/long loop, where a product or component is upgraded and producers involved again (Fig.3, presented in green).
- Business-to-business processes: Long loop, where a product or component loses its original function (Fig.3, presented in blue).
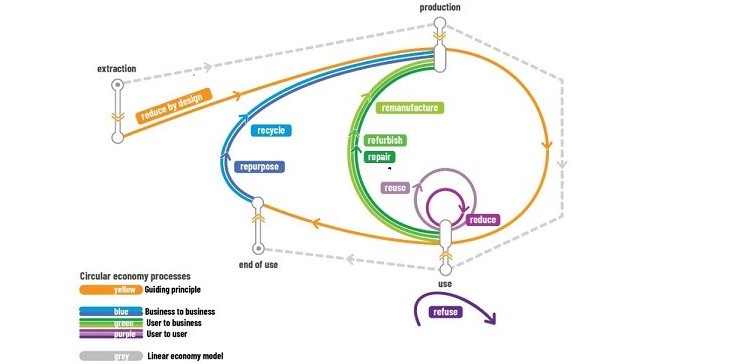
- Reduce by design: reducing the amount of material used, particularly raw material, applied as an overall guiding principle from the earliest stages of design of products and services. It is basic principle of eco-design or sustainable design.
- From a user-to-user perspective: Refuse, Reduce and Re-use.
- From a user-to-business intermediary perspective: Repair, Refurbish and Remanufacture.
- From business-to-business: Repurpose and Recycle.
- 450 million fewer tons of EU carbon emissions by 2030;
- Savings of €600 billion for EU businesses (8% of their annual turnover);
- More than 1 million new jobs from new business models and new businesses from closing the loop of product lifecycles.
Figure 3: Building circularity upon value retention loops
(according to The circular economy: New or Refurbished as CE 3.0?)
Circular processes contributing to circularity can be grouped into 4 categories (Tab.1), from the most impactful to the least:
Re-mining and Recovery of energy are processes used to manage waste, but the value of the material is consumed once, and not put back into the loop. Therefore, these processes are not listed in circular processes.
Table 1. Circular economy processes
| Guiding principle | User to user | User to business | Business to business |
| Reduce by design | Refuse | Repair | Repurpose |
|
| Reuse | Refurbish | Recycle |
|
| Reduce | Remanufacture |
|
Further benefits from circular economy
Circular economy concept sets out large number of ways to "close the loop" of product lifecycles. It puts a major emphasis on finding new, innovative means to move away from a 'take-make-dispose' culture, for instance by recycling and re-using products for longer.
This approach helps to drive forward not just environmental, but also economic progress. According to the European Commission analysis given in the last document: Action plan for circular economy, implementation of the circular economy strategic concept can offer major benefits:
Starting with development and Implementation of roadmap for circular economic society adaptation in one country mainly should be based on three interconnected elements: Circular Economy (business models), Circular Change (legislation and policies) and Circular Culture (citizens and stakeholders).
-
Climate finance
21-01-2022 -
Tackling Climate Change & Air Pollution in the City of Skopje
30-04-2018 -
Tackling Climate Change & Air Pollution in the City of Skopje
22-03-2018 -
Micronarratives
08-06-2022
{{"article.lastestPosts"|translate}}
-
The Chamber of Commerce of North Macedonia has created the first decarbonization guide for small businesses in the country
30-10-2025 -
COP29 UN Climate Conference Agrees to Triple Finance to Developing Countries, Protecting Lives and Livelihoods
02-12-2024 -
We are building partnerships to implement a just energy transition
06-12-2023 -
Energy transition will be accelerated through the Green Financing Facility
06-12-2023



 Мод за знаковен јазик
Мод за знаковен јазик Говорен асистент
Говорен асистент Означи линкови
Означи линкови

 Зголеми маус
Зголеми маус